Tummy Muscle Separation in Pregnancy - It's a needed & necessary thing.
Tummy muscle separation is a necessary part of pregnancy. At TPS our pregnant patients are often concerned about the changes they are observing in their tummy muscles. But we assure you that these changes are a normal and necessary adaptation that occurs in 66-100% of pregnant women.
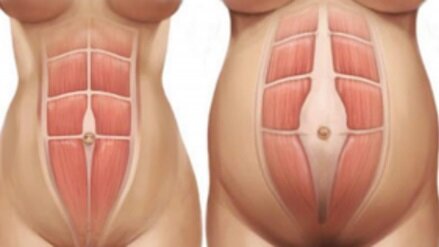
Tummy muscle separation (known medically as rectus abdominis diastasis) refers to an increased distance between your abdominal muscles. To explain this further let’s first talk about your anatomy
Your left and right abdominal muscles join together at the front via a central ligament/connective tissue called your linea alba (easy to remember by thinking about actress Jessica Alba).
During pregnancy, rising hormone levels change your connective tissues, making them stretchier. This softens your linea alba, allowing the gap between your tummy muscles to widen. This thinning and widening of your linea alba creates room for your baby.
In your third trimester, about an 8cm gap between your abdominal muscles is considered normal. As stated previously, these changes occur to create room for your growing baby but also to preserve the function of your abdominal muscles. In other words, if your linea alba widens that means your tummy muscles won’t have to lengthen quite as much. This will in turn preserve your core and its ability to stabilise and support your trunk and pelvis.
As your linea alba thins and widens you may start to notice doming in the centre of your tummy with coughing, laughing, getting out of bed, leaning back and with certain exercises.
Although tummy muscle separation is a normal and necessary part of your pregnancy, we don’t know if doming in the centre of your tummy is bad for you or not. We just don’t have any research on this to guide us. So until we know more, our current recommendation is to modify your exercises and activities of daily living to avoid/minimise abdominal doming with activity.
Doming is ultimately a sign that the load on your tummy, and the build up of intra-abdominal pressure (the pressure inside your tummy), is beyond the capabilities of your linea alba, causing it to bulge/herniate forward. THEORETICALLY if excessive doming occurs repetitively it may result in further thinning and subsequent weakening of the linea alba. This may lead to a poor abdominal recovery postnatally, such as excessive or prolonged tummy muscle separation and/or abdominal hernia.
However, we don’t want doming to hold you back from exercising and keeping strong. Avoiding exercise due to fear avoidance can result in a weaker core and reduced general fitness. This can negatively impact your pregnancy, birth (you need strong core muscles to push effectively) and your postnatal recovery!
Staying active and performing tailored core exercises throughout your pregnancy optimise your core muscle function and can help to minimise/reduce the occurrence of doming with day to day life and with exercise.
If you notice abdominal doming please seek the advice of one of our friendly physios. At TPS we are strong advocates for prenatal and postnatal physiotherapy assessments being a standard part of care. A prenatal/postnatal assessment includes a thorough abdominal assessment, reviewing the function of your core.
Reference: Mota et al. 2018 Normal width of the inter-recti distance in pregnant and post - partum primiparous women.